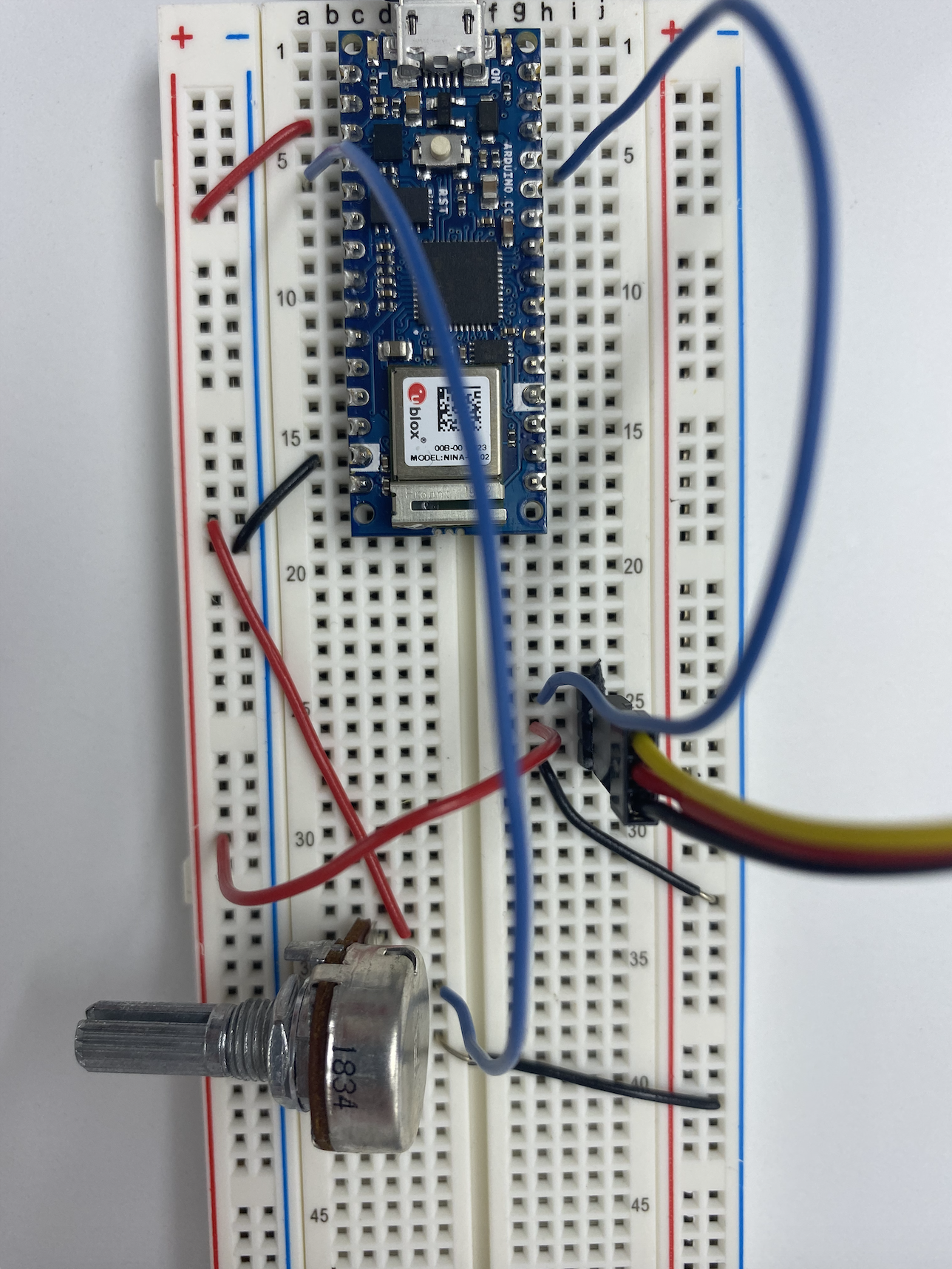
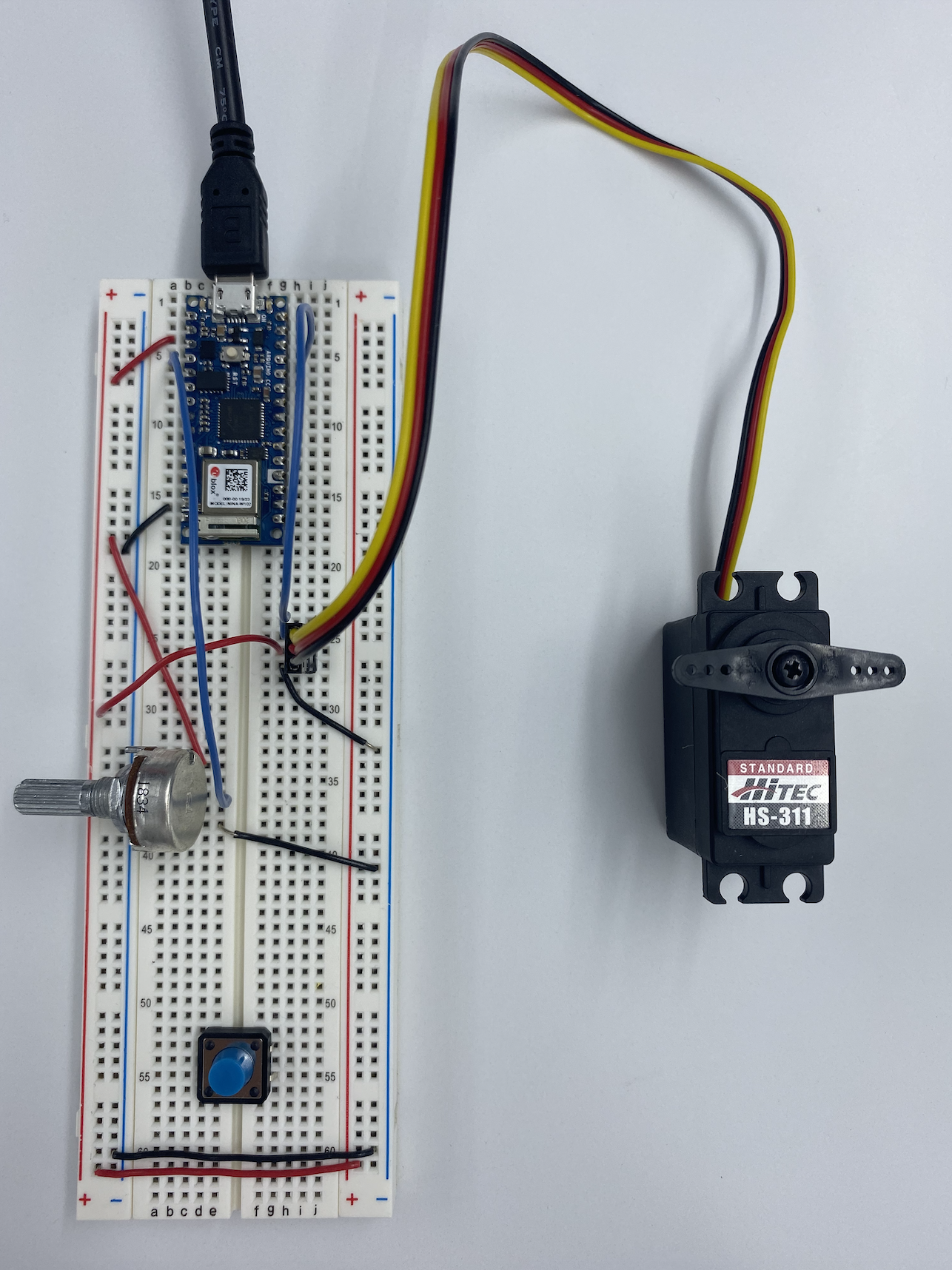
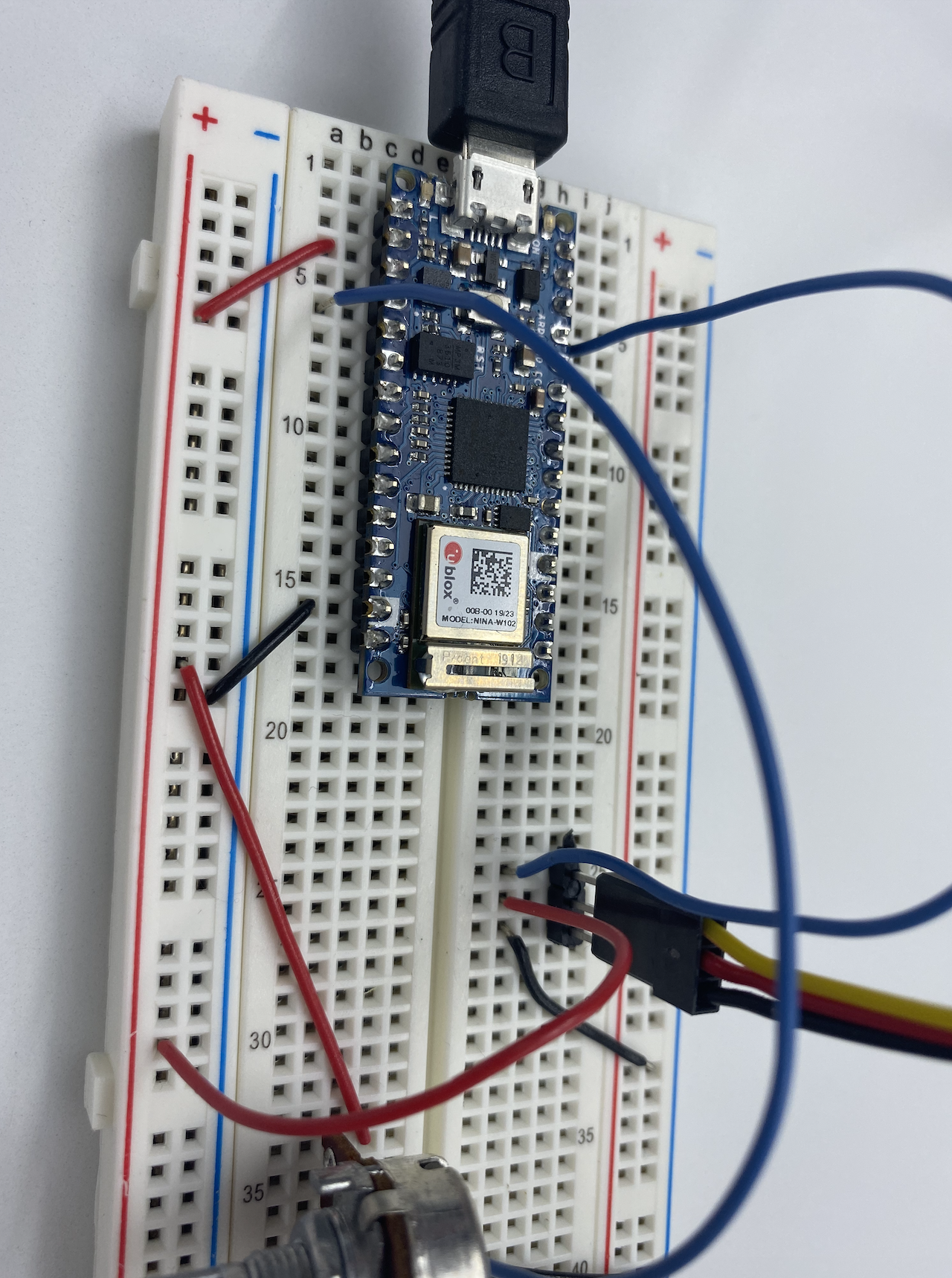
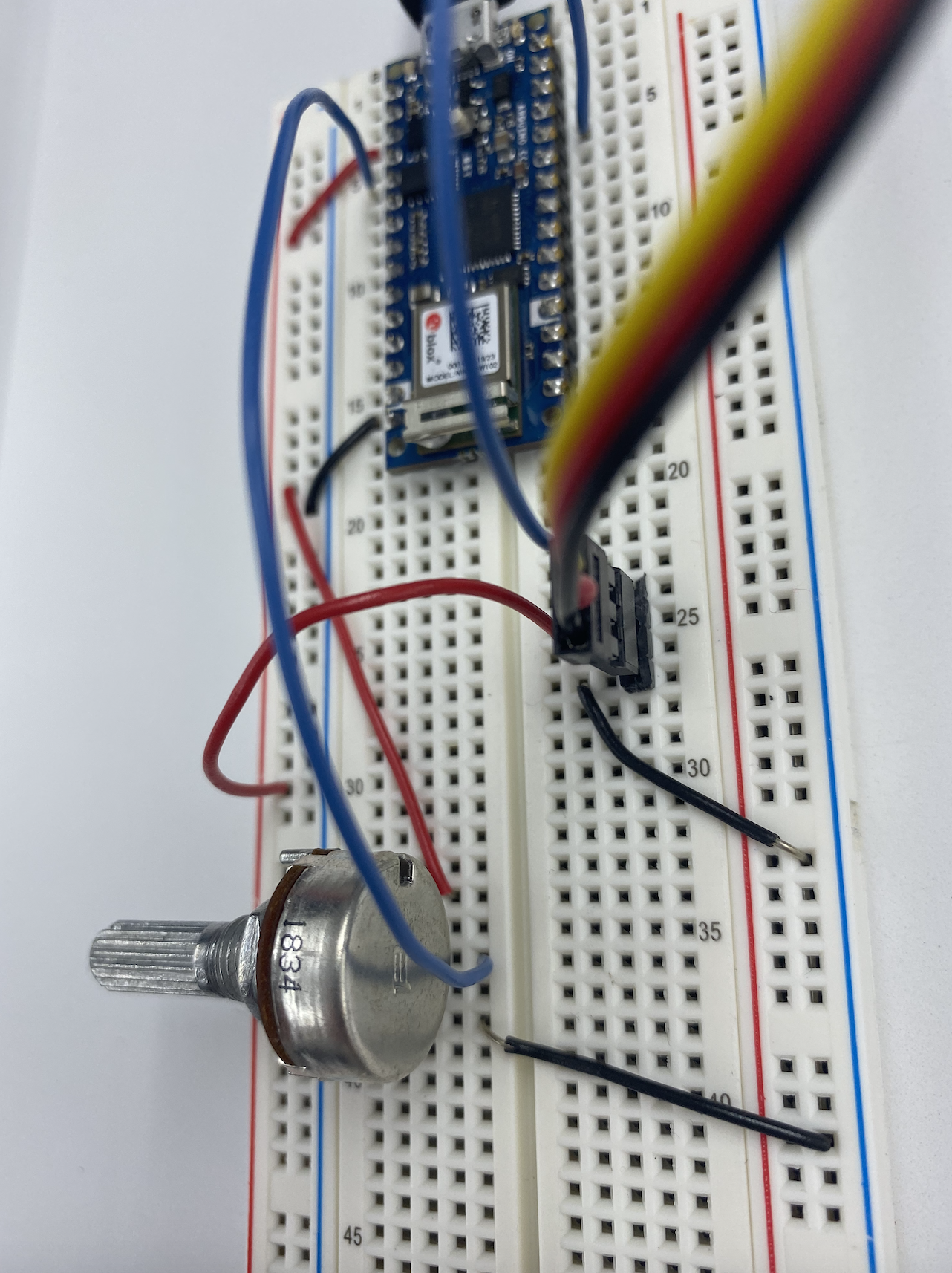
//1. Find out range of sensor void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // initialize serial communications } void loop() { int analogValue = analogRead(A0); // read the analog input Serial.println(analogValue); // print it }
//2.Map the result into 0-179 void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // initialize serial communications } void loop() { int analogValue = analogRead(A0); // read the analog input Serial.println(analogValue); // print it int servoAngle = map(analogValue, 0, 1023, 0, 359); //}
So I had a questions on this step.
Where does 9600 come from: ‘Serial.begin(9600)’
Where does 1023 come from: ‘int servoAngle = map(analogValue, 0, 1023, 0, 179)’
//3. #include <Servo.h> // include servo library Servo servoMotor; int servoPin = 9; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); servoMotor.attach(servoPin); } void loop() { int analogValue = analogRead(A0); Serial.println(analogValue); //0-1023 int servoAngle = map(analogValue,0,1023, 0,360); Serial.println(servoAngle); servoMotor.write(analogValue);
Creative Application
Idea sketch